Core JAVA
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
Java overview
Java basics
Java Objects and classes
Java Constructors
Java basic datatypes
Java variable types
Java modifiers/Access Modifiers In Java
Java Basic Operators
Java Loops and Controls
Java conditions
Java numbers and characters
Java strings
Java arrays
Java date time
Java methods
Java file and IO operations
Java exceptions
Inner class
Java OOPs Concepts
Java Inheritance
Java Polymorphism
Java Abstraction
Java Encapsulation
Java Interface
Cohesion and Coupling
Association, Aggregation and Composition
Java Collections
Java ArrayList
Java LinkedList
Set and HashSet
LinkedHashSet and TreeSet
Queue and PriorityQueue
Deque and PriorityQueue
Java Map Interface
Java HashMap
Internal Working Of Java HashMap
Java Mutithread
Methods of Thread In Java
Join , run & Start Method in Threads
Difference b/w start & run Methods in Threads
Java Concurrency Package & its Features
CountDownLatch, CyclicBarrier, Semaphore and Mutex in Thread
Association, Aggregation and Composition
Association
- Association is a relation between two classes. To achieve association we used objects of classes.
- Association can be of between one to one, one to many, many to one and many to many objects of classes.
One to One:
If single class object has some relation with another single object of a class then it is called one to one association.
One to Many:
If single class object has some relation with more than one object of a class then it is called one to many association.
Many to One:
If multiple objects of class has relation with one object of class then it is called many to one relationship.
Many to Many:
If multiple objects of a class has relation with another multiple objects of class then it is called many to many relationship.
Aggregation and composition are forms of association.
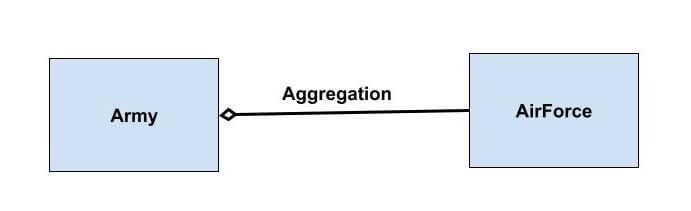
Aggregation
Aggregation is a form of association where one class has an object(s) of another class in such a way that destruction of any one of class object wont destroy another, they are loosely associated.
Aggregation is called has-a relation.
Example:
Army has AirForce and AirForce has Pilot, in this example destruction of one does not necessary means another can’t exist.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Army {
final AirForce airForce;
Army(AirForce airForce) {
this.airForce = airForce;
}
}
class AirForce {
final List pilots;
AirForce(List pilots) {
this.pilots = pilots;
}
}
class Pilot {
String name;
int age;
}
public class AssociationExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pilot pilot = new Pilot();
List pilots = new ArrayList();
pilots.add(pilot);
AirForce airForce = new AirForce(pilots);
Army army = new Army(airForce);
}
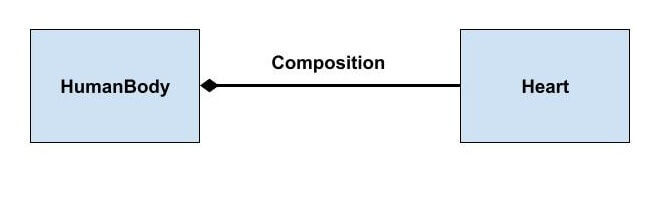
} Composition
class Heart {
}
class HumanBody {
Heart heart = new Heart();
} UML of Association, Aggregation and Composition
UML diagram of Association:
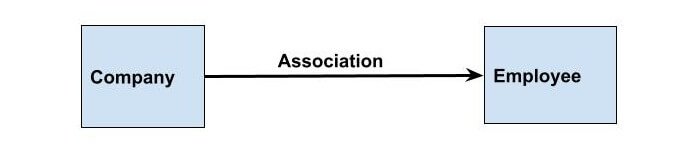
UML diagram of Aggregation:
UML diagram of Composition:
Generalization and Specialization
Generalization:
Generalization is a process where we define a parent or super class for smaller child classes and by doing that we are generalizing different smaller classes to one super or parent class.
Generalization is a bottom up approach.
Generalization can be achieved by creating sub classes and their one parent class.
Example:
Car class is generalized from ElectricCar and PetrolCar sub classes.
Specialization:
Specialization is a process where we define child or sub classes from one super class which are more specific and specialized in details.
Specialization is a top down approach.
Example:
Sub classes ElectricCar and PetrolCar from parent Car class is an example of specialization.
Diagram of Generalization and Specialization:

References
Reference article from oracle: UML
