Core JAVA
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
Java overview
Java basics
Java Objects and classes
Java Constructors
Java basic datatypes
Java variable types
Java modifiers/Access Modifiers In Java
Java Basic Operators
Java Loops and Controls
Java conditions
Java numbers and characters
Java strings
Java arrays
Java date time
Java methods
Java file and IO operations
Java exceptions
Inner class
Java OOPs Concepts
Java Inheritance
Java Polymorphism
Java Abstraction
Java Encapsulation
Java Interface
Cohesion and Coupling
Association, Aggregation and Composition
Java Collections
Java ArrayList
Java LinkedList
Set and HashSet
LinkedHashSet and TreeSet
Queue and PriorityQueue
Deque and PriorityQueue
Java Map Interface
Java HashMap
Internal Working Of Java HashMap
Java Mutithread
Methods of Thread In Java
Join , run & Start Method in Threads
Difference b/w start & run Methods in Threads
Java Concurrency Package & its Features
CountDownLatch, CyclicBarrier, Semaphore and Mutex in Thread
Java Inheritance
What is Inheritance
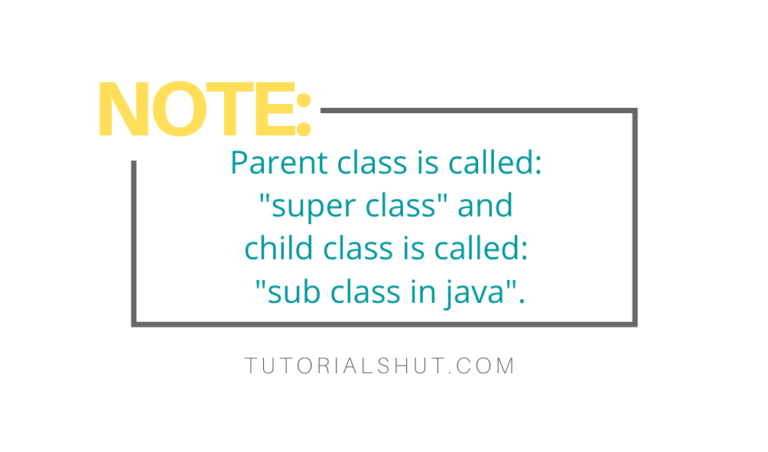
Inheritance means inheriting something in OOP, if a class inherits behaviour of another class it is called inheritance and class which is being inherited is called parent or super class and class which inherits parent class is called child or subclass. We look in detail on Java Inheritance in this article.
By using inheritance we can bring methods and other variables to the child class from the parent based on access level and use them as they are part of child class.
Benefits of Inheritance
- Reusability – By inheritance we can bring parent class’ method and variables to the child class like they are part of child class and no need to write their definitions in child class.
- Reduces Code and Effort – It helps in reducing code and effort in child classes if the parent already has desired methods and properties.
- Maintenance – It is easy to maintain we update definition in parent and automatically new definition is available to child
Example Of Java Inheritance With Extends
In java to inherit properties of parent class we can used extend key word with child class definition and inherit property of parent class.
class Sup {
//Code
}
Class Sub extends Sup {
//Code
} 
Java Inheritance Example
Below is an example of inheritance where Car class is parent or super class and ElectricCar is child or sub class. Child class ElectricCar has inherited startCar() and stopCar() methods from parent Car class and using it.
class Car {
public void startCar() {
System.out.println("Car started.");
}
public void stopCar() {
System.out.println("Car stopped.");
}
}
class ElectricCar extends Car {
public void typeOfCar() {
System.out.println("This is electric car.");
}
} public class InheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ElectricCar electricCar = new ElectricCar();
//inherited methods startCar() and stopCar() is available to child class ElectricCar
electricCar.startCar();
electricCar.stopCar();
electricCar.typeOfCar();
}
} Output:
Car started.
Car stopped.
This is electric car.
What is Super and Its Use
In java super is a reserved keyword is which represents parent class and its properties for example if you want to call constructor of super class in child you can add super() in child class constructor.
If you want to access methods and variables of super class which are similar or same in child, you can user super.<method/variable name> to access it.
In below example you can see in ElectricCar class acessSuperClassMethods() is accessing super class methods and variables using super keyword.
Example:
class Car {
String carCompany = "Ford";
public void startCar() {
System.out.println("Car started.");
}
public void stopCar() {
System.out.println("Car stopped.");
}
}
class ElectricCar extends Car {
public void typeOfCar() {
System.out.println("This is electric car.");
}
public void startCar() {
System.out.println("Car started in child.");
}
public void stopCar() {
System.out.println("Car stopped in child.");
}
public void acessSuperClassMethods() {
super.startCar();
super.stopCar();
System.out.println(super.carCompany);
}
}
public class InheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ElectricCar electricCar = new ElectricCar();
//inherited methods startCar() and stopCar() is available to child class ElectricCar
electricCar.acessSuperClassMethods();
}
}
OUTPUT:
Car started.
Car stopped.
Ford
Invoking Super class Constructor
class Bus {
public Bus(String busName) {
System.out.println("Super constructor, bus name is:"+busName);
}
}
class MiniBus extends Bus {
public MiniBus(String busName) {
super(busName);
System.out.println("Sub constructor, bus name is:"+busName);
}
}
public class InheritanceExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MiniBus miniBus = new MiniBus("Volvo");
}
}
Output:
Super constructor, bus name is:Volvo
Sub constructor, bus name is:Volvo
Type Of Inheritance In Java
class ClassA {
//Parent code
}
class ClassB extends ClassA {
//Child code
} class ClassA {
//Parent code
}
class ClassB extends ClassA {
//Child code
}
class ClassC extends ClassB {
//Child code
} class ClassA {
//Parent code
}
class ClassB extends ClassA {
//Child code
}
class ClassC extends ClassA {
//Child code
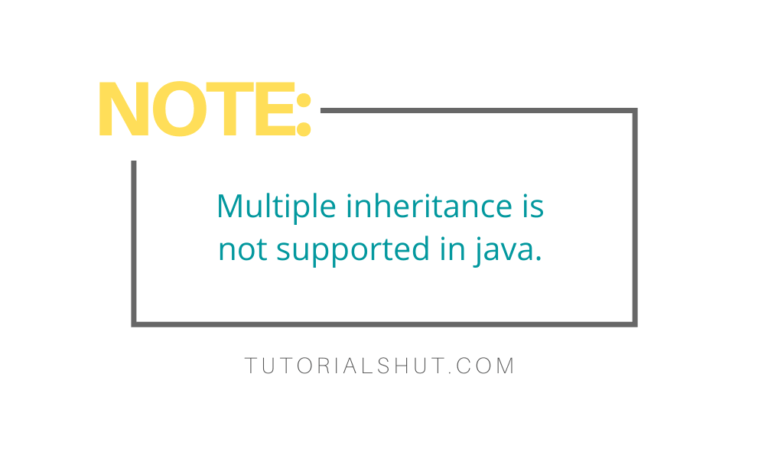
} 4) Multiple Inheritance – If a class inheritance more than one class at same time will be called multiple inheritance, java does not support this due to diamond problem in inheritance.
Has-A and Is-A in Java
Has-A and Is-A is types of relationship between classes, we will see details on these in coming article on Is-A and Has-A in coming chapters.
References:
Refer google this article from google for reference: Inheritance
