Core JAVA
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
Java overview
Java basics
Java Objects and classes
Java Constructors
Java basic datatypes
Java variable types
Java modifiers/Access Modifiers In Java
Java Basic Operators
Java Loops and Controls
Java conditions
Java numbers and characters
Java strings
Java arrays
Java date time
Java methods
Java file and IO operations
Java exceptions
Inner class
Java OOPs Concepts
Java Inheritance
Java Polymorphism
Java Abstraction
Java Encapsulation
Java Interface
Cohesion and Coupling
Association, Aggregation and Composition
Java Collections
Java ArrayList
Java LinkedList
Set and HashSet
LinkedHashSet and TreeSet
Queue and PriorityQueue
Deque and PriorityQueue
Java Map Interface
Java HashMap
Internal Working Of Java HashMap
Java Mutithread
Methods of Thread In Java
Join , run & Start Method in Threads
Difference b/w start & run Methods in Threads
Java Concurrency Package & its Features
CountDownLatch, CyclicBarrier, Semaphore and Mutex in Thread
Java Features, Overview and History
What is Java?
Java is a platform independent object-oriented programming language.

Java History
Java programming language was initially developed by Mr. James Gosling by company Sun Microsystems and released in 1995, first released version was java 1.0 (J2SE).
Between 2006-2007, Sun Microsystem released java along with source code under GNU licence as an open source software.
Currently all rights of java are sold to Oracle from Sun Microsystem though open source versions of java is available and the latest stable java version is java 15.
It was released with the promise of write once, run anywhere (WORA) which means once a program is written the same can be executed on windows or MAC or Linux without any change.
Apart from Java standard edition J2SE later came J2EE (enterprise edition) and J2ME (mobile edition).
Naming convention J2 later was changed to J so J2SE changed to JSE, J2EE to JEE and J2ME to JME.
Java Programming Language Features
1) Object oriented – Java is an object oriented programming language which means that any real life object is represented by java class and object.
Example: Car, House, Tree, Road and Bank Account etc.
These real-world objects can be represented by java objects and required behaviour and attributes can be defined.
In the following chapters, we will cover object-oriented principles in detail, then you will understand the true meaning of it.
2) Platform Independent and simple – Java is a platform independent language that means we can write a java program once and run in different machines and architecture.
Example: If we write java program in windows, the same program can be executed in a MAC or Linux system without any change.
See below pictorial representation:
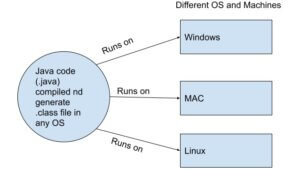
Once java code written and class file generate, it can run anywhere in any another machine or OS.
3) Secure – Java provides robust security features and it is very difficult to corrupt or hack.
4) Architecture neutral and portable – Java generated byte codes from its source code program which can be executed in any operating system and machine architecture hence it is neutral to any machine architecture and portable.
5) Multithreaded – Java gives the ability to program multithreaded applications which means within a program or process you can run smaller tasks in parallel to get high performance.
6) Dynamic – Java can change its behaviour and determine many aspects of a program while execution.
Software Requirement to Develop and Run Java Program
Below softwares are needed:
1) A computer with any OS windows, MAC or Linux.
2) Java JDK (java development Kit)
3) Any editor software, it can be simple notepad or IDE (Integrated Development Environment)
Next Topics to Go Through
In the coming chapters, you may go through key components of java JDK, JRE and JVM.
