Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
Regular Expressions/ Regex Unix
- Regular expressions in Unix is a pattern consisting of a sequence of characters that is matched against the text.Mostly grep command is used in conjugation with regex.
- Regex in Unix evaluates text against the pattern, if they match, the expression is true and a command is
executed.
In this article , we will cover below topics:
What is Regex in Unix?
- Used when one wants to search for specific lines of text containing a particular pattern
- String of ordinary and metacharacter which can be used to match more than one type of pattern
- Used in grep, egrep, awk, vi, sed etc. to match a group of similar patterns.
Some examples of metacharacters are:
[ ], ^, $, { }, ., etc
Grep with regex
SYNTAX :
grep [option...] pattern [file...]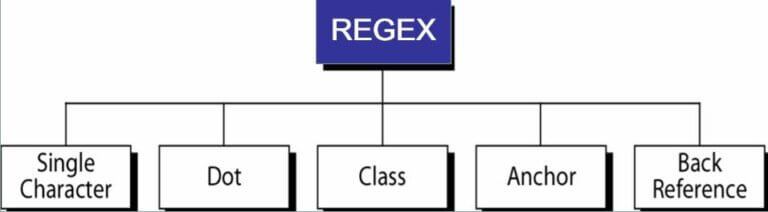
Basic Regular Expressions Unix:
Expression Use
[ ]: Matches any one of a set characters
[ ] with hyphen: Matches any one of a range characters
^: The pattern following it must occur at the beginning of each line
^ with [ ] : The pattern must not contain any character in the set specified
$: The pattern preceding it must occur at the end of each line
. (dot): Matches any one character
\ (backslash): Ignores the special meaning of the character following it
*: zero or more occurrences of the previous character
(dot).*: Nothing or any numbers of characters.
Examples of Basic regular expressions with grep command:
[ ]
- Matches any one of a set characters in the text.
- The character set to be used in the matching process is enclosed in brackets.
- A range of text characters is indicated by a dash (-). [a-d]
Example:
$grep “Test[abc]” filenameSearch pattern will be:
Testa , Testb or Testc
2. Use [ ] with hyphen/ dash
- Matches any one of a range characters
Example:
$grep “Test[1-5]” filenameIt specifies the search pattern as
Test1 , Test2, Test3 , Test4, Test5
3. Use ^
- The pattern following it must occur at the beginning of each line
$grep “^Test” filenameSearch lines beginning with Test.
Search pattern will be like:
Testing ,Testers, Testable, Tester etc.
$ls –l |grep “^d” Display list of directories only
$ls –l |grep “^-” Display list of regular files only
4. Use ^ in [ ]
- The pattern must not contain any character in the set specified
$grep “Test[^a-c]” filenameIt specifies the pattern having word “Test” followed by any character other than an ‘a’,’b’, or ‘c’
5. Use $
- The pattern preceding it must occur at the end of each line
$grep "ing$" filenameSearch pattern will be like:
Testing ,eating, sitting etc.
6. Use . (dot)
- Matches any one character
$grep ".est" filename7. Use \ (backslash)
- Ignores the special meaning of the character following it
$grep "Test\.\[abc\]" file.txtIt specifies the search pattern as Test.[abc]
$grep "M\.A" file.txtIt specifies the search pattern as
M.A
8. Use *
- zero or more occurrences of the previous character
$grep "[aA]gg*[ar]wal" filename9. Use (dot).*
- Nothing or any numbers of characters.
$grep "M.*A" filenameInterval Regular Expressions Unix
- tell us about the number of occurrences of a character in a string.
Expression Use
{n} Matches the preceding character appearing ‘n’ times exactly
{n,m} Matches the preceding character or expression immediately before appearing ‘n’ times but not more than m
{n, } Matches the preceding character only when it appears ‘n’ times or more
\+ Matches previous character one or more times
\? Matches previous character 0(zero) or one time only
1. Use {n}
- Matches the preceding character appearing ‘n’ times exactly
$ cat test.txt
Sitting
Eating
Rating
$cat test.txt | grep -E t\{2}
Output: Sitting2. Use {n,m}
- Matches the preceding character appearing ‘n’ times but not appearing more than m times
$ cat test.txt
Sitttting
fitting
Rating
$cat test.txt | grep -E t\{2,3}
Output: fitting2. Use \+
- Matches previous character one or more times
$ cat test.txt
Sitting
fitting
Rating
filter out lines where character ‘i’ precedes character ‘t’
$ cat test.txt | grep "i\+t" Output: Sitting fitting
Some practical example for regex:
1. Matching a word by ignoring its case
$ grep "[Tt]utor"
2. Matching mobile number using regex with grep
3. Match email-address
$ grep -E "[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,6}"4. Finding files with a particular extension
$ ls -l | grep '.csv$'
For more on regex refer here
Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
