Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
Text Processing Unix Commands
Text processing Unix commands are those affecting text and text files. For example, commands like cut, paste, cmp, sort, comm, head, tail, wc, diff, grep are few in the list. While editing files, you may lose track of what changes you have made to which files.
In this article, we will cover commands that compare files.
cmp command in Unix
- Compare 2 files byte by byte.
- It is mostly useful for scripts as it only reports whether the files are different or not.
- Helps to find out whether the two files are identical or not.
When cmp is used for comparison between two files, it reports the location of the first mismatch to the screen if difference is found and if no difference is found i.e the files compared are identical. cmp displays no message and simply returns the prompt if the files compared are identical.
SYNTAX: cmp [OPTION] file1 file2
Options can be:
-c :Output differing bytes as characters. -i N :Ignore differences in the first N bytes of input. -l : Write the byte number (decimal) and the differing bytes (octal) for each difference. -s : Write nothing for differing files; return exit statuses only. -v : Output version info
Example 1: lets consider two files :
$ cat file1.txt My name is Mohan $ cat file2.txt My name is Mohit
1. Compare file1 to file2 and outputs results
$ cmp file1.txt file2.txt OUTPUT: file1.txt file2.txt differ: byte 15, line 1
2. Skip same number of initial bytes from both input files
$ cmp -i 3 file1.txt file2.txt file1.txt file2.txt differ: byte 12, line 1
So we see that the initial 3 bytes were skipped
Example 2:
$ cat file1.txt My name is Mira $ cat file2.txt My name is Mira $cmp file1.txt file2.txt $ _
/*indicating that the files are identical*/
diff command in Unix
-
-
- Reports the differences between files.
- Compares files line by line.
- It is useful when record level differences are to be traced.
- Tells which lines in one file have to be changed to make the two files identical.
- If the files match, no output is produced.
- diff uses certain special symbols and instructions that are required to make two files identical
-
Special symbols are:
-
-
- a : add
- c : change
- d : delete
-
SYNTAX: diff [option...] file1 file2
|
Options |
Use |
|
-i |
Ignores the case differences |
|
-c |
Compares two program code differences |
|
-q |
Reports whether file differ or not |
Example:
$cat test1.txt sam sam Tom Tom Tom
$cat test2.txt Tom Tom Tom Tom Tom
$diff test1.txt test2.txt Output: 1,2c1,2 < sam < sam — > > Tom
The output 1,2c1 means that the lines from 1,2 in the first file need to be changed to match the line number 1 in the second file. Lines preceded by ‘<‘ are lines from the first file. Lines preceded by ‘>’ are lines from the second file.
comm command in Unix
-
-
-
- Compares 2 sorted files line by line
- Produces 3 column output when no Options are passed.
- Column 1 contains line unique to first file
- Column 2 contains line unique to second file
- Column 3 contains line common to both files
-
-
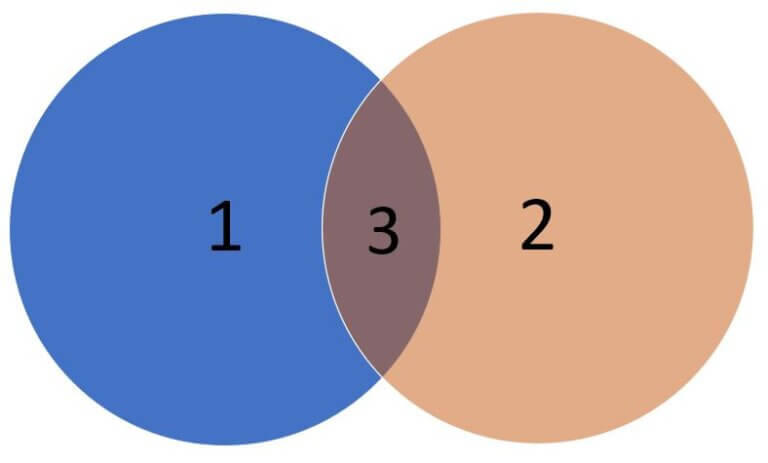
SYNTAX:
$ comm file1 file2Options | Use |
-1 | does not print column 1 (lines unique to file 1) |
-2 | does not print column 2 (lines unique to file 2) |
-3 | does not print column 3 (lines common to both files) |
–check-order | Verify files are in sorted order |
–nocheck-order | Ignore even if files are not in sorted order |
Example:
$ cat test1.txt sam sam Tom Tom Tom
$ cat test2.txt Tommy Tommy Tom Tom Tom
$ comm test1.txt test2.txt sam sam Tommy Tommy Tom Tom Tom
The output of comm command produces 3 columns.
1. First contains data specific to test1.txt
2. Second contains data specific to test2.txt
3. Third contains lines common to both the file
For more details on file comparison in Unix refer here
Recommended Articles:
Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
