Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
Unix Links ( Symbolic links)
Unix links, also known as a symlink or symbolic links, is a special type of file that points to another file or directory.
We will learn below topics in this article:
What is a link in Unix?
- A link in UNIX is a pointer to a file.
- Creating links is a kind of shortcut to access a file.
There are two types of links :
- Hard Link
- Soft Link or Symbolic Links
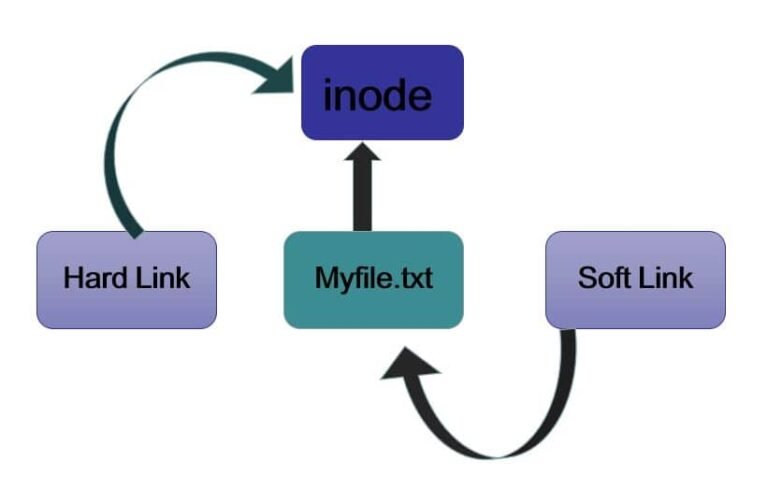
Hard link
- Both the original file and hard linked file have the same inode numbers, therefore they reference the same physical file location.
- If the original file is deleted , the link is not deleted, hard links are more flexible
- Are more efficient (in terms of access time) as compared to soft links.
- This can not be used to link a file on another file system, or to link directories
Syntax:
$ ln [original filename] [link name] Soft link
- The original file and the link have different inode numbers. Each soft linked file points to the original file
- When the original file is deleted, the link remains as an invalid link and will not behave correctly. It is called as hanging link
- Soft Link contains the path for original file, if original file is removed it impacts the link functionality
- This can be used to link file on a different file system
- Can be used to link directories
Syntax:
$ ln -s [original filename] [link name]
How to Use the ln Command to create Unix Links
ln command in Unix is used for creating links between files. By default, the ln command creates hard links.
To create a symbolic link, use the -s (–symbolic) option.
1. Create link to a file
SYNTAX: ln -s [OPTIONS] FILE LINK
If both the FILE and LINK are given, ln will create a link from the file specified as the first argument (FILE) to the file specified as the second argument (LINK).
If only one file is given as an argument or the second argument is a dot (.), ln will create a link to that file in the current working directory . The name of the symlink will be the same as the name of the file it points to.
on successful execution , no output is displayed but returns zero.
2. Creating Symlink To a File
To create a symbolic link to a given file use -s option:
SYNTAX: ln -s FILE symbolic_link
The symbolic_link parameter is optional. The ln command will create a new link in your current directory in case it is not mentioned.
The -> symbol shows the file the symlink points to.
3. Create Symlinks to a Directory
Directory name is used as the first parameter and the symlink as the second parameter.
SYNTAX: ln -s DIRECTORY LINK
Example:s

4. Overwriting Symlinks
If you try to create a symbolic link that already exists , the ln command will print an error message.
To overwrite the destination path of the symlink, use the -f (–force) option.
SYNTAX: ln -sf FILE LINK
5. Removing Symlinks
unlink or rm command is used to remove the links from file or directory.
SYNTAX:
unlink LINKNAME
or
rm LINKNAMERecommended Articles:
Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
