Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
Unix Process Commands : ps, nice, kill, nohup, time
We will learn about processes in Unix and some essential Unix process commands that allow us to view ongoing processes in our terminal like ps Unix command, nice Unix command, kill Unix command, nohup Unix command, time Unix command and top.
Below topics are covered in this article:
- What is a Process?
- Types of process: Foreground process and background process
- Top command in Unix
- PS command in Unix
- Kill command in Unix
- NICE command in Unix
- NOHUP command in Unix
- TIME command in Unix
What is a Process?
Any running program or a command given to a system is called a process. A process could run in foreground or background.
A process is a program in execution.
-
- Each process is allocated a process identifier or PID.
- In general , each process is started by another process, known as parent process.
Types of processes in Unix
There are two types of unix process:
Foreground Processes Unix:
-
- It runs on the screen and needs user input, hereafter you have to wait for its completion before being able to enter a new command.
- It is also referred as interactive process.
- For example, MS Office power point, Word etc.
Background Processes Unix:
-
- It runs in the background and usually do not need user input. Unlike foreground processes, when a background process has been executed you don’t have to wait for its completion to execute some other command.
- It is also referred as non-interactive process.
- For example ,system scanning using antivirus.
Any command can be run as a background process by typing a space and ‘&’ after the command.
SYNTAX: $ <command>&
Example for foreground and background process:
$ ls pwd
During the execution o above command, no other processes can be run or started as the prompt would not be available.
Press Ctrl-c which will send a kill signal to any process running in foreground, terminating it immediately or press Ctrl-z to send a suspend signal to any process running in the foreground, pausing it immediately.
Top command in Unix
It is used to show all the running processes within the working environment along with their memory and CPU usage.
Syntax:
$ top
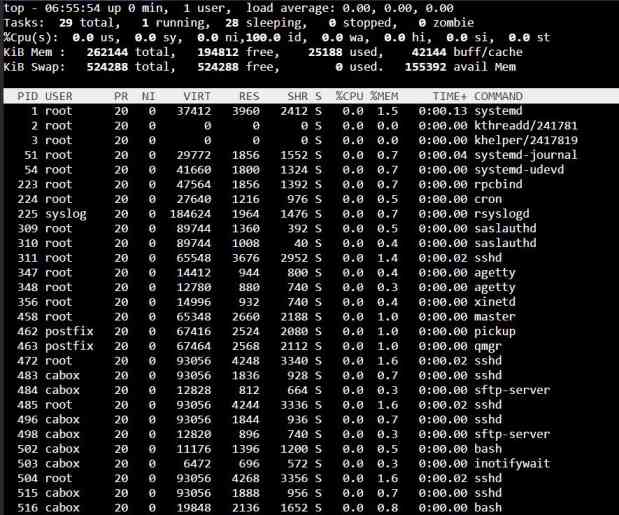
Output fields are:
- PID: Unique Process ID given to each process.
- User: Username of the process owner.
- PR: Priority given to a process while scheduling.
- NI: ‘nice’ value of a process.
- VIRT: Amount of virtual memory used by a process.
- RES: Amount of physical memory used by a process.
- SHR: Amount of memory shared with other processes.
- S: state of the process
- ‘D’ = uninterruptible sleep
- ‘R’ = running
- ‘S’ = sleeping
- ‘T’ = traced or stopped
- ‘Z’ = zombie
- %CPU: Percentage of CPU used by the process.
- %MEM :Percentage of RAM used by the process.
- TIME+: Total CPU time consumed by the process.
- Command: Command used to activate the process.
ps command in Unix
ps stands for ‘Process Status’ and displays information about a selection of the active processes.
If you want a repetitive update of the selection and the displayed information, use top instead.
- gives the details about the processes
- Option –f gives full listing
- Option –e or –A displays all processes
To see every process on the system using standard syntax:
ps -e
ps -ef
ps -eF
ps -ely 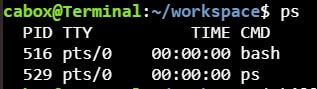
The output fields are:
PID :process ID TTY :terminal type TIME: total time the process has been running CMD :name of the command that launches the process
nice command in Unix
nice command in unix is used to execute utility or shell script with a particular CPU priority, thus giving the process more or less CPU time than other processes.
- A niceness of -20 is the highest priority and 19 is the lowest priority.
- Default value is 0
- Execute commands with lower priority.
SYNTAX:
nice [option] command [arguments]
You can change the nice value of a process that is already running by using renice command
SYNTAX:
renice [value] -p [PID]
kill command in Unix
Unix has no stop command instead it has kill command. Kill is used to send a signal to a process. The most commonly used signal is “terminate” (SIGTERM) or “kill” (SIGKILL). However, there are many more. The full list can be shown with kill -l.
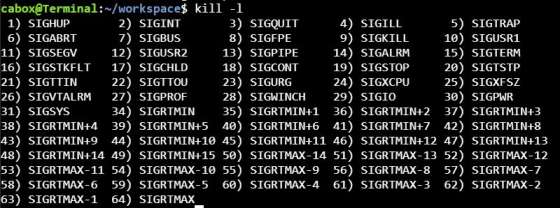
- Send signals to processes.
- The default signal is 15, which is SIGTERM.
SYNTAX: kill -[option] pid
the process with particular pid will be terminated.
nohup command in Unix
- Nohup means no hang up . It is a command that keep processes running even after exiting the shell or terminal.
- Nohup prevents the processes or jobs from receiving the SIGHUP (Signal Hang UP) signal.
- This is a signal that is sent to a process upon closing or exiting the terminal
- Continue execution even after logout.
SYNTAX: nohup command [arguments]
or
nohup options
Checking the version of Nohup
You can begin by checking the version of Nohup using the syntax below:
SYNTAX: nohup --versionStarting a process in the background using Nohup
To start a process in the background use the & symbol at the end of the command.
SYNTAX: nohup command &Example: nohup ping google.com & —–we are pinging google.com and sending it to the background.
Killing a Nohup process running in background
- When a command is put in the background for running using
nohup, the background operator (&) will give you the PID at the command prompt. - If your plan is to manually manage the process, you can save that PID and use it later to kill the process if needed, via
kill PIDorkill -9 PID(if you need to force kill). - You can also get PID later on by
ps -ef | grep "command name"and then usekill PIDorkill -9 PID(if you need to force kill).
time command in Unix
The time command is used to determine how long a given command takes to run. It is useful for testing the performance of your scripts and commands.
- Displays time usage of a command
Syntax:
time [option] [COMMAND]
- Displays time usage of a command
for more details refer here
Recommended Articles:
Unix For Testers
Unix System Architecture
Unix File System Structure
Absolute and Relative Path
Basic Unix Commands
cal command in Unix
who command in Unix
date command in Unix
clear command in Unix
more command in Unix
whoami command in Unix
uname command in Unix
man command in Unix
echo command in Unix
Unix File System Commands
ls command in Unix
cat command in Unix
cp command in Unix
mv command in Unix
pwd command in Unix
cd command in Unix
mkdir command in Unix
rmdir command in Unix
rm command in Unix
touch command in Unix
dirname command in Unix
tar command in Unix
Unix Links(ln)
Hard Link
Soft Link
Regular Expressions
Basic Regular Expressions
Interval Regular Expressions
Pipes and Filters
Unix Text Processing Commands
cmp command in Unix
diff command in Unix
comm command in Unix
cut command in Unix
Paste command in Unix
head command in Unix
tail command in Unix
wc command in Unix
sort command in Unix
grep command in Unix
Process Related Command
top command in Unix
ps command in Unix
nice command in Unix
Kill command in Unix
nohup command in Unix
time command in Unix
File Tranfer Commands in Unix
file transfer using scp command
file transfer using rlogin command
file transfer using telnet command
ssh(Secure Shell) command in Unix
ftp file transfer command
sftp file transfer command
chmod command in Unix
File Permission and File Security in Unix
