Cypress tutorials
what is cypress?
cypress architecture
Selenium & cypress Architecture
cypress features
Cypress Installation and project setup
node-js
Visual Studio Code
Create New Project in Cypress
Open and start Cypress
cypress executable location
cypress open
Switch browser in cypress
Run TestCase in cypress
cypress Test Runner
cypress command line
Basic Test Case in Cypress
Mocha test framework in cypress
Describe and it in cypress
Basic test case
Hooks in Cypress
before() Hooks in Cypress
beforeEach() Hooks in Cypress
after() Hooks in Cypress
afterEach() Hooks in Cypress
Default assertion in cypress
When not to assert in cypress
How to modify default assertion timeout
Assertions in cypress
Implicit assertion using should & and
How to use should & and for assertion
Explicit assertion using should & and
How to use expect in assertion
Common assertions in cypress
Basic Comands in cypress
Custom Comands in cypress
Custom command syntax & command.js
Parent custom commands in cypress
Child custom commands in cypress
Dual custom commands in cypress
Example of cypress custom commands
Variables & Aliases in cypress
Return Values In Cypress
Closures in cypress
Variables and Aliases in Cypress
Typically in Cypress you hardly need to ever use variables like const, let, or var for variable declaration.This is because of the Asynchronous API nature in Cypress.
Using closures we can access the objects that were yielded to you without assigning them.
Below will be covered as part of this article:
- Why is it hard to work with variables in Cypress?
- Return Values In Cypress
- Closures in cypress
- Variables in cypress
- Aliases in cypress
- How to access aliases in cypress?
Why is it hard to work with variables in Cypress?
- When we write a Cypress test, it seems that each command is a statement and will execute sequentially, but that’s not the case.
- Each command you write in a Cypress test is added to a queue of commands, each of which will be executed in order asynchronously when the test runs.
- This asynchronous nature of commands enables one of Cypress’s greatest features that is automatic waiting for each command.
But it also means you can’t return values from one command and use that value in the next command.
// this won't work the way you think it does const button = cy.get('Agreebtn') button.click()
Remember how all Cypress commands are asynchronous? In JavaScript, asynchronous is handled with promises. Cypress commands are a specific implementation of promises.
The return value isn’t an element – it’s a Cypress version of a promise!
To access what each Cypress command yields you use .then().
Return Values In Cypress
All the Cypress commands are enqueued and run asynchronously. Therefore, we cannot assign or interact with any return values of any Cypress commands. We will see a little example of the same.
// this won't work the way you think it does const button = cy.get("Agreebtn"); //this command is to get the element with the button attribute button.click()
Closures in cypress
The return value in the above example isn’t an element – it’s a Cypress version of a promise!
To access what each Cypress command yields you use .then().We call these closures.
cy.get("Agreebtn").then(($btn) => { // store the button's text const txt = $btn.text(); });
Variables in cypress
Variables are used to store information to be referenced and manipulated in a computer program.
In Cypress we usually do not use much of const, let, or var as we always have access to the objects that were yielded to you without assigning them.
When dealing with mutable objects (that change state) where we often want to compare an object’s previous value to the next value, variables are useful.
Example:
cy.get('#num').then(($span) => {
// we are capturing the number by assigning it to a variable
const num1 = parseFloat($span.text())
cy.get('button')
.click() //we have clicked the button once
.then(() => {
// we are capturing the number again by assigning it to another variable
const num2 = parseFloat($span.text())
// we are ensuring that num1+1 is equal to num2
expect(num2).to.eq(num1 + 1)
})
})
Since span is changing its state every time we click the button, we can assign it to a variable to compare its present and previous state.
Aliases in cypress
- In the above examples we have got the ‘txt’ of the button. We aren’t going to use it right away, so we want to store it somewhere that our test can access it later.
- Cypress provides a feature named “aliases” for storing variables for future use.
- Specifically, we’ll use the .as() command to alias a value.
- .as(), like all commands, can only be called from a Cypress chain, with accessing the cy global object.
How to access aliases in cypress?
Sharing context:
- Sharing context is the simplest way to use aliases.
- Specifically, we’ll use the .as() command to alias a value.
- The primary use case for sharing context is dealing with cy.fixture – which is to load a fixed set of data in a file.
- @ character is used for accessing aliases.
Using Aliases with Fixtures
Oftentimes you may load a fixture in a beforeEach hook but want to utilize the values in your tests.
Example:

Sample Code:
// <reference types="cypress" />
describe('Aliases Example', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
// alias the example fixtures
cy.fixture('example.json').as('example')
})
it('utilize fixtures details using aliases', () => {
// use the special '@' syntax to access aliases
cy.get('@example').then((details) => {
// access the users argument
const name = details.name
// user's name
cy.log(name)
const title = cy.visit("https://tutorialshut.com/").title().should('contain', details.name);
})
})
})
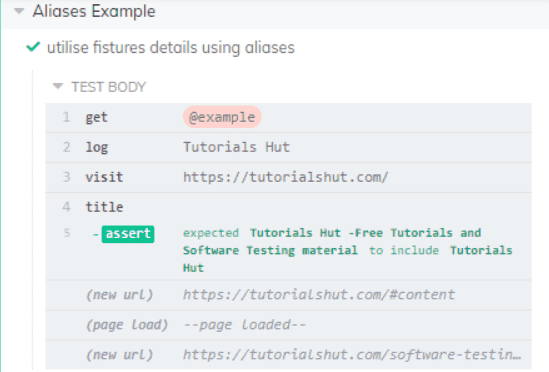
Output on executing the test in cypress:
Elements as aliases:
- Aliases have other special characteristics when being used with DOM elements.
- After you alias DOM elements, you can then later access them for reuse.
Example:
// alias all of the tr's found in the table as 'rows'
cy.get('table').find('tr').as('rows')
Cypress tutorials
what is cypress?
cypress architecture
Selenium & cypress Architecture
cypress features
Cypress Installation and project setup
node-js
Visual Studio Code
Create New Project in Cypress
Open and start Cypress
cypress executable location
cypress open
Switch browser in cypress
Run TestCase in cypress
cypress Test Runner
cypress command line
Basic Test Case in Cypress
Mocha test framework in cypress
Describe and it in cypress
Basic test case
Default assertion in cypress
When not to assert in cypress
How to modify default assertion timeout
Assertions in cypress
Implicit assertion using should & and
How to use should & and for assertion
Explicit assertion using should & and
How to use expect in assertion
Common assertions in cypress
Basic Comands in cypress
Custom Comands in cypress
Custom command syntax & command.js
Parent custom commands in cypress
Child custom commands in cypress
Dual custom commands in cypress
Example of cypress custom commands
Variables & Aliases in cypress
Return Values In Cypress
Closures in cypress
