Testing Foundation
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
Equivalence partitioning and Boundry Value Analysis
Equivalence partitioning and Boundary value analysis are the techniques used to reduce the number of scenarios to test.
Equivalence Partitioning Method is also known as Equivalence class partitioning (ECP).
We are explaining the most important manual software testing techniques.
The topics discussed in this article are:
Equivalence partitioning
- It is also known as Equivalence Class Partitioning (ECP)
- It is a specification-based or black box testing technique
- The input data is divided into different equivalence data classes – which are generally termed as ‘Valid’ and ‘Invalid’.
- Test only one condition from each partition or equivalence.
- It reduces the number of test cases to a finite list of testable test cases covering maximum possibilities
- Inputs are divided into groups that are expected to behave similar
- Can be done for valid and invalid partitions
- This can be applied at all levels/phases of testing
- Partitions are also called Classes
Example:
Suppose In Login page A username field accepts character limit of 2 – 200 inclusive. Here, there would be three partitions: one valid partition and two invalid partitions.

The valid partition: Between 2 & 200 characters. (Username field should handle all inputs with 2-200 characters)
The first invalid partition: less than 2 character any. Value for e.g. 1 (When less than 2 characters are entered, text field should reject the value)
The second invalid partition: > 200 (text field should reject all values which are greater than 200)
Boundary Value analysis
-
- Boundary value analysis is a selection of test cases that takes boundary values as inputs. It is based on the assumption that errors are usually found on boundaries.
- It can be applied at all levels/phases of testing
- Boundaries are good place to look for defects
- Boundary Value Analysis is the next part of Equivalence Partitioning for designing test cases where test cases are selected at the edges of the equivalence classes.
- It is also a part of stress and negative testing.
- For each range, there are two boundaries, the lower boundary (start of the range) and the upper boundary (end of the range) and the boundaries are the beginning and end of each valid partition
Example:
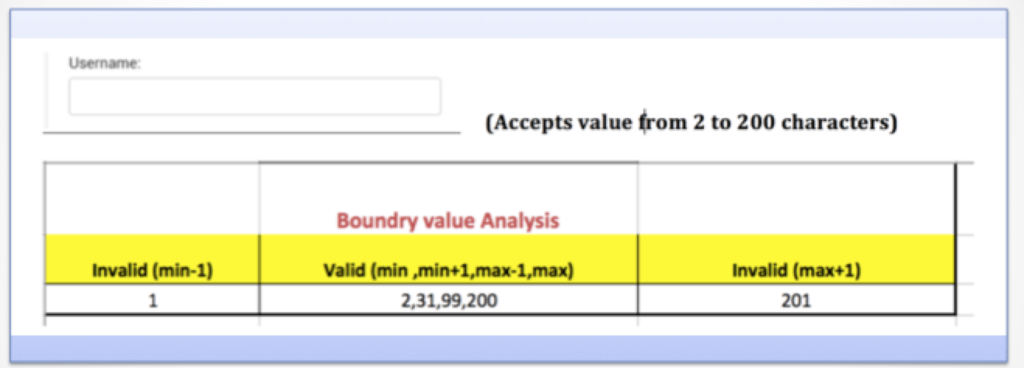
A username on login page field accepts character limit of 2 – 200 inclusive.
Testing Foundation
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
