Testing Foundation
Basics of Software Testing
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
Software Quality Factors & McCall Quality Model
- Software quality factors can be divided into three broad measures: operability, maintainability and transferability.
- Each of these measures can be further broken down as shown in Figure
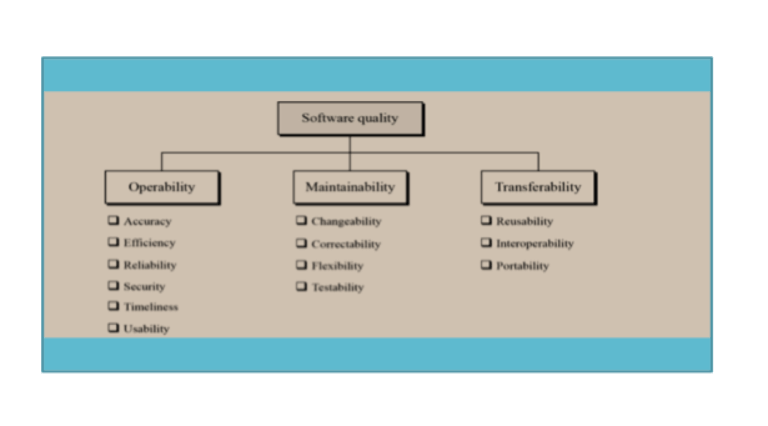
1) McCall (consist of 11 factors, 1977)
2) Deutsch and Willis (consist of 12 to 15 factors, 1988)
3) Evans and Marciniak (1987)
Mccall’s software quality factors
McCall software quality model was introduced in 1977 .It is divided the software requirements into 11 software quality factors.
These are divided into three categories – Product operation, Product revision, and product transition factors.
- Product operation factors − Correctness, Reliability, Efficiency, Integrity, Usability.
- Product revision factors − Maintainability, Flexibility, Testability.
- Product transition factors − Portability, Reusability, Interoperability.
The definition of these 11 software quality factors is given below:
- Correctness – extent to which a program satisfies its specification and fulfills the client’s objective.
- Reliability – extent to which a program is supposed to perform its function with the required precision.
- Efficiency – amount of computing and code required by a program to perform its function.
- Integrity – extent to which access to software and data is denied to unauthorized users.
- Usability– labor required to understand, operate, prepare input and interpret output of a program
- Maintainability– effort required to locate and fix an error in a program.
- Flexibility– effort needed to modify an operational program.
- Testability– effort required to test the programs for their functionality.
- Portability– effort required to run the program from one platform to other or to different hardware.
- Reusability– extent to which the program or it’s parts can be used as building blocks or as prototypes for other programs.
- Interoperability– effort required to couple one system to another.
Recommended Articles:
Testing Foundation
Basics of Software Testing
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
