Testing Foundation
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
What are seven Software Testing principles ?
Software testing is a critical process in the software development lifecycle that aims to identify defects, errors, and gaps in the software system. To ensure that the testing process is effective and efficient, there are seven principles of testing that should be followed. There are seven Software Testing Principles that every software tester should know.
Below are the 7 Principles of Software Testing
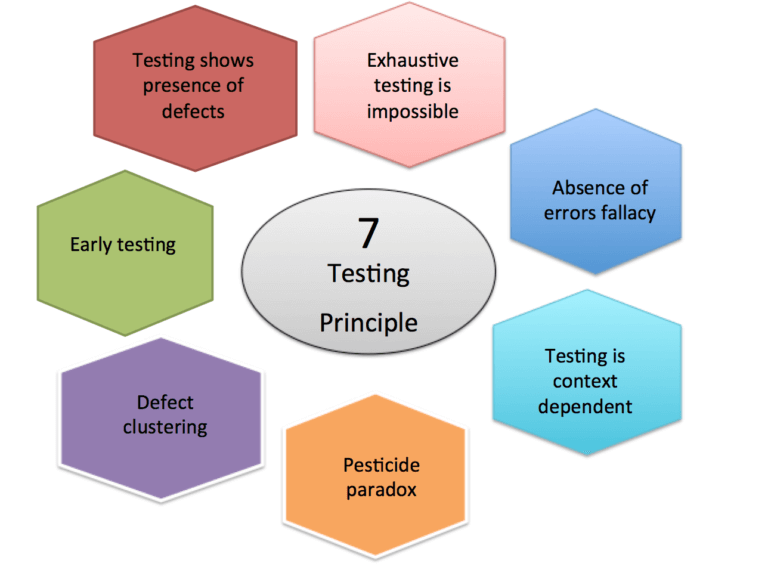
Seven software Testing principles
1 – Testing shows a presence of defects
- It is important to remember that testing shows the presence of defects and not their absence, thorough testing will give everyone confidence that the software will not fail.
- Testing shows presence of defects principle does not confirm that any software is completely correct and completely devoid of issues.
- Testing reduces the probability of undiscovered defects remaining in the software but even if no defects are found, it is not a proof of correctness.
2 – Exhaustive testing is impossible
- Software tester can’t test all combinations of inputs and preconditions ,it is absolutely impossible to test EVERYTHING .
- Instead of testing all combinations, do risk analysis and prioritise to focus testing efforts.
- One of the skills of testing is assessing risks and planning your tests around these – you can then cover vast areas, while making sure test the most important functions.
3 – Early Testing (saves time and money)
- Testing early is important in the software lifecycles because amending the code or issue at this stage is a lot easier and cheaper than doing at the end of the product’s lifecycle,
- Start testing early to find defects.
- Software tester should always focus on test objectives.
4 – Defect Clustering
- A small number of modules contain most of the defects detected.
- As per Pareto’s Principal or 80 – 20 Rule 80% of Defects are Caused by 20% of code.
- Once these areas have been identified, so focus testing on the sensitive areas.
- Testing effort should be focused proportionally to the defect density
5 – Pesticide Paradox
- If the same tests are repeated over and over again, eventually the same set of test cases will no longer find any new bugs.
- To overcome ‘pesticide paradox’, the test cases need to be regularly reviewed and revised, and new and different tests need to be written to exercise different parts of the software to potentially find more defects.
6 – Testing is context dependent
- Different software products have varying requirements, functions and purposes so same tests should not be applied across all.
- Tester might use a different approach, techniques, and types of testing depending upon the application type.
- For example, testing of the e-commerce site is different from the testing of the Banking site.
7 – Absence-of-errors fallacy
- Finding and fixing defects doesn’t help if the system is unusable or does not meet users’ needs and expectations
- For example -sometimes 99% of the defect-free software can remain unusable if the software is developed with the wrong requirements.
So these are the Seven Software Testing Principles. Everyone should be aware and understand these seven principles of software testing as these are called as the pillars for testing. By adopting these principles, software development teams can increase the chances of identifying and fixing defects early in the development process, which will result in a more reliable and stable software system.
Recommended Articles:
Testing Foundation
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
