Testing Foundation
Basics of Software Testing
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
Integration testing: Definition, Importance, strategies/approaches
This article will present you with a complete idea about integration testing definition, strategies , importance etc.
We will learn below topics in this article
What is Integration Testing?
It is a type of testing to check if different modules work together as a whole.The purpose is to find faults in the interaction between integrated units.
- Main traditional strategies can be classified as top-down integration, bottom-up integration, big-bang integration.
- We reconsider these strategies in an object-oriented environment.
- Various factors like cost, complexity of the application etc determine which approach is selected.
The purpose is to expose faults in the interaction between integrated units. Once all the modules have been unit tested, integration testing is performed.
It is second level of testing performed after Unit Testing and before System Testing.Interaction between integrated components is called Component Integration testing.
For more on definition refer link.
Importance:
- Helps to build real-time use cases during the end to end testing.
- Improves test gaps and helps in better test coverage.
- Tests are reliable and it is easy to isolate failures.
- Integration tests detects issues such as database connection issue, connecting queues down etc.
Advantages:
- Attain confidence that integrated modules work properly.
- The tester can start testing once the modules to be tested are available.
- Detects errors related to the interface between modules by helping modules interact with API’s and other third-party tools.
Process :
- Prepare Integration Test Plan.
- Prepare integration test scenarios and test cases.
- Create test automation scripts.
- Execute test cases.
- Report the defects.
- Track and retest the defects once fixed by developers.
Strategies for integration:
- Top Down integration testing
- Bottom Up integration testing
- Big Bang integration testing
Big Bang Testing
- Big Bang testing is a type of testing where all the components are integrated together at once and then tested as a whole.
- Individual modules are not integrated until and unless all the modules are ready.
- All the modules are integrated without performing any integration testing and then it’s executed to know whether all the integrated modules are working fine or not.
Top Down Testing
- First Test the top layer or the controlling subsystem or Start with the ‘‘root’’ and one or more called modules.
- Then combine all the subsystems that are called by the tested subsystems and test the resulting collection of subsystems
- Do this until all subsystems are incorporated into the test
- Stubs are needed to do the testing.
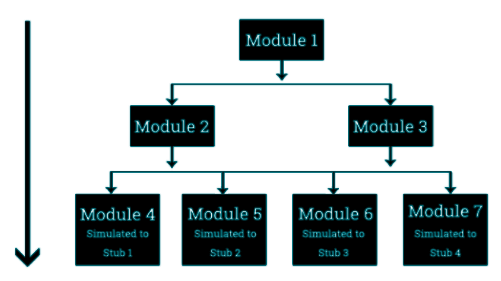
Bottom Up Testing
- The subsystems in the lowest layer of the call hierarchy are tested individually.
- Then the next subsystems are tested that call the previously tested subsystems
- This is repeated until all subsystems are included
- Drivers are needed.

Sandwich/Hybrid Testing
This is an approach which is a combination of Top Down and Bottom Up approaches.
