Testing Foundation
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
Test Plan in software Testing |Definition , Activities etc
Test Plan is the most important activity undertaken by a test leader in any test project as it involves creating a roadmap for the entire testing process.
The goal of test planning is to ensure that testing is conducted in a systematic and organized manner and that the software system meets the desired quality and functionality requirements. Test planning includes creating a comprehensive test plan, which outlines the objectives, scope, approach, and schedule of the testing process.
This article will present you with a complete idea about TestPlan , Test Activities , entry and exit criteria etc.
We will learn below topics in this article
What is Test Plan?
- A critical component of test planning is the creation of a test strategy that outlines the testing approach and methods to be used for testing the software system.
- Test Plan is the most important activity undertaken by a test leader in any test project.
- Test strategy should take into account the type of software being developed, the target audience, and the criticality of the software system
- Ensures there is a list of tasks and milestones in a baseline plan to track progress .
- Provides accurate test effort
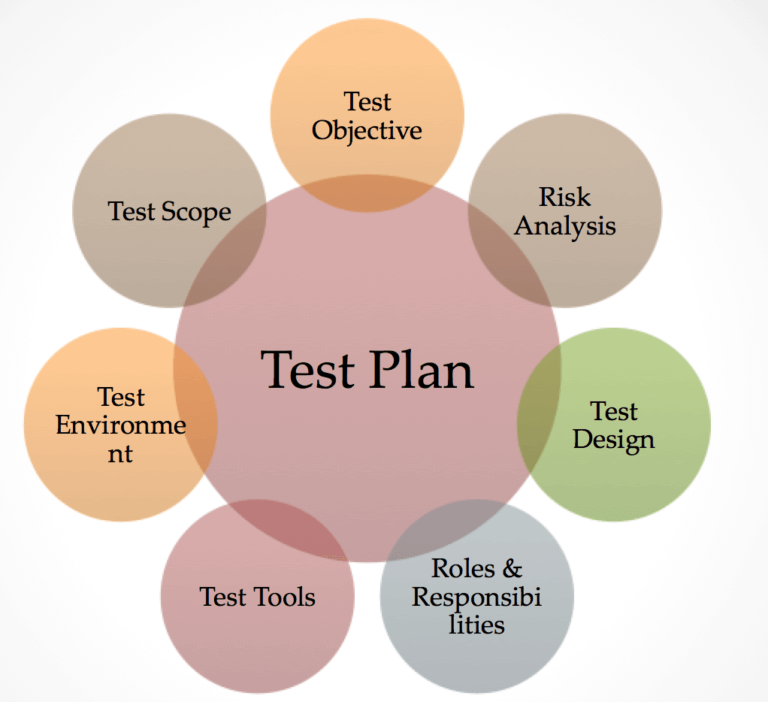
Test Plan Activities
- Test Plan Activities determine the scope and risks that need testing, involve the Project Manager
- Identify and agree on the objectives of testing, with a focus on TIME, QUALITY and COST.
- A Test Strategy (Overall Approach) ensures that test levels, entry criteria and exit criteria are defined
- Making decisions
- Features to test?
- What roles will perform the testing activities?
- When and how the testing activities should be done?
- How the test results will be evaluated?
- Exit criteria
- Create a Plan to identify when and who will undertake the test analysis and design activities along with the documentation of the schedule for test implementation, test execution and test evaluation
- Decide on the format of test project documentation, and which plans and test cases will be documented.
- Define Management information including the metrics required, establishing processes to monitor and control test preparation and execution along with defect resolution and risk issues.
- Ensure that test documentation generates test assets i.e. test cases.
ENTRY CRITERIA
- Entry Criteria in Test Plan defines when to start testing
- Can include the start of a level of testing, start of test design and/or start of test execution.
- The stages of Entry Criteria to Test Execution are as follows:
- Test tools installed in the environment which should be ready for use.
- Testable code is available.
- All test data is available and correct.
- All test design activity has completed.
EXIT CRITERIA
- Exit Criteria in Test Plan is used to decide when a test activity has been completed or needs to stop.
- Exit Criteria can be defined for all test activities such as planning, specification and execution or for a specific test level for test specification and execution.
- Exit Criteria should have been agreed as early as possible in the life cycle.
Typical exit criteria are:
- Estimates of defect density or reliability measures
- Functionality or risk
- Thoroughness measures, such as coverage of code,
- Residual risks, such as defects not fixed or lack of test
Test plan includes the following components:
Introduction:
This section provides an overview of the testing process, including the scope, objectives, and approach.
Test Objectives:
This section outlines the goals and objectives of the testing process, including the expected outcome of the testing.
Testing Scope:
This section defines the scope of the testing process, including the features and functionalities to be tested, the types of testing to be conducted, and the testing environment.
Testing Approach:
This section outlines the testing approach to be used, including the testing techniques, tools, and methods.
Test Schedule:
This section outlines the timeline for the testing process, including the testing phases, milestones, and deadlines.
Test Deliverables:
This section defines the deliverables of the testing process, including the test plan document, test cases, test scripts, and test reports.
Test Environment:
This section describes the testing environment, including the hardware, software, and network configurations.
Roles and Responsibilities:
This section outlines the roles and responsibilities of the testing team members, including the test manager, test analysts, and testers.
IEEE-829 Test Plan
- TestPlan Identifier
- References
- Introduction
- Test Items
- Software Risk Issues
- Features to be Tested
- Features not to be Tested
- Approach
- Item Pass/Fail Criteria
- Suspension Criteria and Resumption
- Requirements
- Test Deliverables
- Remaining Test Tasks
- Environmental Needs
- Staffing and Training Needs
- Responsibilities
- Schedule
- Planning Risks and Contingencies
- Approvals
- Glossary
SPACE DIRT = IEEE829 TestPlan
S – Scope test items, what to test, what not to test
P – People training, responsibilities, schedule
A – Approach the approach that will be taken to testing
C – Criteria entry/exit criteria, suspension/resumption criteria
E – Environment test environment needs
D – Deliverables what is being delivered as part of the test
process
I – Incidentals introduction, identification (of the document),
approval authorities
R – Risks risks and contingencies
T – Tasks the test tasks that are involved in the testing
process.
Recommended Articles:
Testing Foundation
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
