Testing Foundation
Basics of Software Testing
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
Iterative Model (Incremental Model) in SDLC
- In Iterative Model ,the process of defining requirements, designing, building and testing a system, completed as a series of shorter development cycles.
- Software development process where requirements are divided into several stand-alone software development modules.
- Produces and delivers the working component at each increment of the project.
- There are few examples of iterative Models are : prototyping, Rapid Application Development (RAD), Rational Unified Process (RUP) and agile development models.
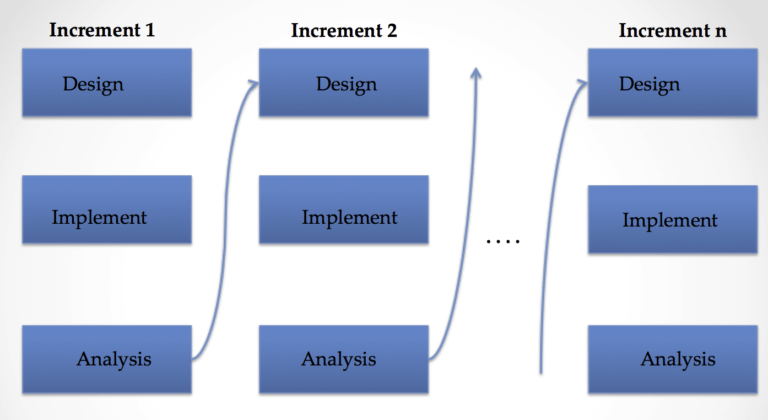
Phases of incremental Model
Requirement analysis
- Product analysis expertise identifies the functional requirements and non-functional requirements.
- Product analysis expertise communicates with the customer and note down all the requirements of the customer.
Design & Development
- The design phase defines how the system will accomplish what was defined in the Requirement analysis phase.
- In the design phase, all components of the system are defined.
Implementation
- Coding is done for developing software.
- Design, which is finalised in designing phase, is now implemented practically and the coding is completed.
- Programs are coded in small units to implement the working product
Testing
- The goal of the testing phase is to find errors, which means that a good testing strategy is the one that finds most errors.
- Examines the performance of each existing function as well as additional functionality.
Advantages of Iterative Model
- Errors are easy to detect.
- Easier to test and debug during a smaller iteration
- More Flexible, hence less costly to change scope and requirements.
- Lowers initial delivery cost.
- Easy to manage risk because it is managed through iteration.
Disadvantages of Iterative Model
- Needs good planning and design.
- Total cost is higher than waterfall.
- Needs well-defined module interfaces.
When to use the Incremental model?
- This model can be used when the requirements of the whole system are clearly defined and understood.
- There is a need to get a product to the market early.
- Resources with required skill sets are not available
- There are some high-risk features and goals.
Recommended Articles:
Testing Foundation
Basics of Software Testing
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
What is Software Testing?
Objective of Testing
Why is testing necessary?
Common Terms used in Testing
Verification Vs Validations
QA Vs QC
Debugging Vs Testing
Seven Testing Principles
SDLC Vs STLC
Fundamentals of Test Process
Software quality Factors
Software Development Models
Waterfall Model
V models
Iterative Model
Test Levels
Component Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Strategies for Integration Testing
Big Bang
Stubs and Driver
Top Down Testing
Bottom Up Testing
Test Types
Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing
Structural Testing
Re-testing & Regression Testing
Static AND Dynamic Techniques
Static Technique
Dynamic Technique
Static Analysis by Tools
White Box Techniques
Statement Coverage Testing
Branch Coverage Testing
Decision Coverage Testing
Path Coverage
Black Box Techniques
Equivalence Partitioning
Boundary Value Analysis
Decision Table testing
State Transition testing
Experience Based TestingTechniques
Random Testing
Exploratory Testing
Error Guessing
Functional Testing
Integration Testing
Unit Testing
System Testing
Smoke testing
Sanity testing
Regression Testing
Usability Testing
Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing
White Box & Black Box Testing
Globalization & Localization Testing
Non Functional Testing
Compatibility testing
Endurance testing
Load testing
Performance testing
Recovery testing
Scalability testing
Stress testing
Volume testing
Test Planning and Estimation
Test Planning
Test Strategies Vs Test Plan
Test Approaches
Risk and Testing
Product Risks
Project Risks
Defect Management
Defect LifeCycle
Severity Vs Priority
